Overview¶
Wi-SUN is a wireless communication standard aiming to enable large-scale IOT networks in a mesh structure. The network typically consists of line powered routers and gateways, and battery powered end nodes. The Wi-SUN FAN Specification is given by the Wi-SUN Alliance.
In TI Wi-SUN FAN Stack, the 6LoWPAN, RPL, IPv6, ICMPv6 and UDP layers have been adapted from open source components. An overview of the SW components is given in Figure 19.
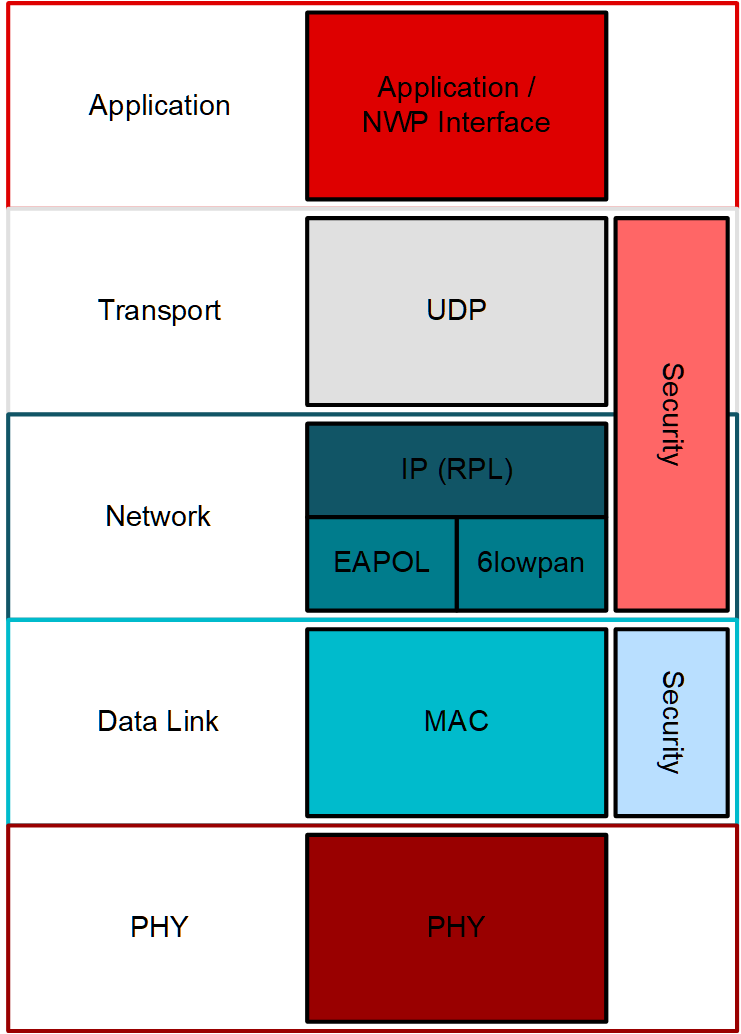
Figure 19. TI Wi-SUN FAN Stack Overview¶
What is a FAN?¶
FAN - field area network is a network type aiming for connectivity on a larger scale. Example uses are within a smart city. To achieve this, the FAN consists of multiple smaller personal area networks (PANs). The FAN can connect to a Wide area network (WAN) in order to grow the scale even more.
Within each PAN, nodes assume one of three operational roles (set via the local administrative policy):
Each PAN contains a Border Router providing WAN connectivity to the PAN. The Border Router maintains source routing tables for all nodes within its PAN, provides node authentication and key management services, and disseminates PAN wide information such as broadcast schedules.
Router node, which provides upward and downward packet forwarding (within a PAN). A Router also provides services for relaying security and address management protocols.
Leaf nodes provide minimum capabilities: discovering and joining a PAN, send/receive IPv6 packets, etc. (Leaf node role is not implemented in TI Wi-SUN FAN.)
The node roles and network leves are visualized in Figure 20.
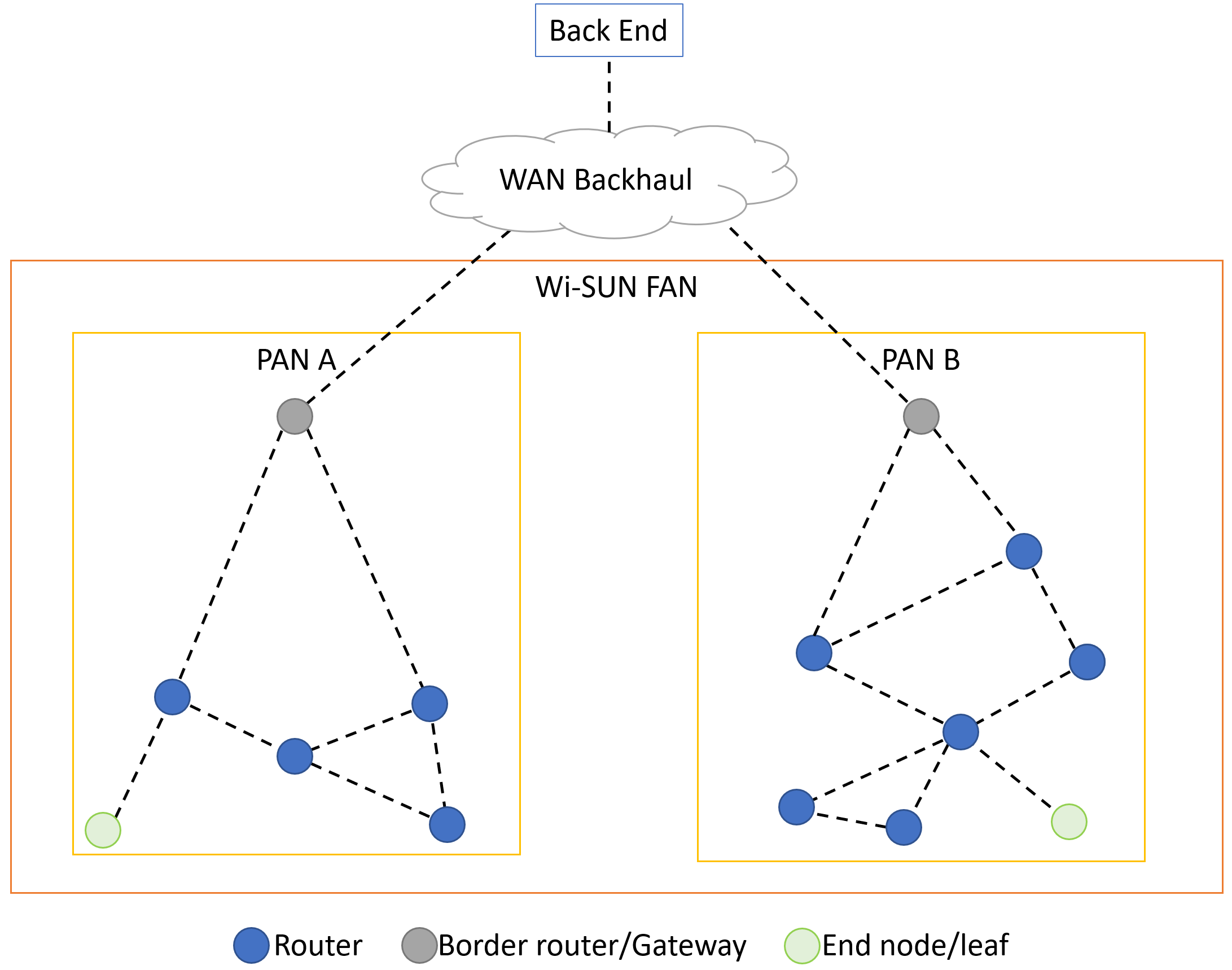
Figure 20. FAN Overview¶
Architecture Choices¶
TI Wi-SUN FAN Stack can be used in two separate architectures based on the end product application. Figure 21. shows the two different system architectures enabled by TI Wi-SUN FAN Stack.
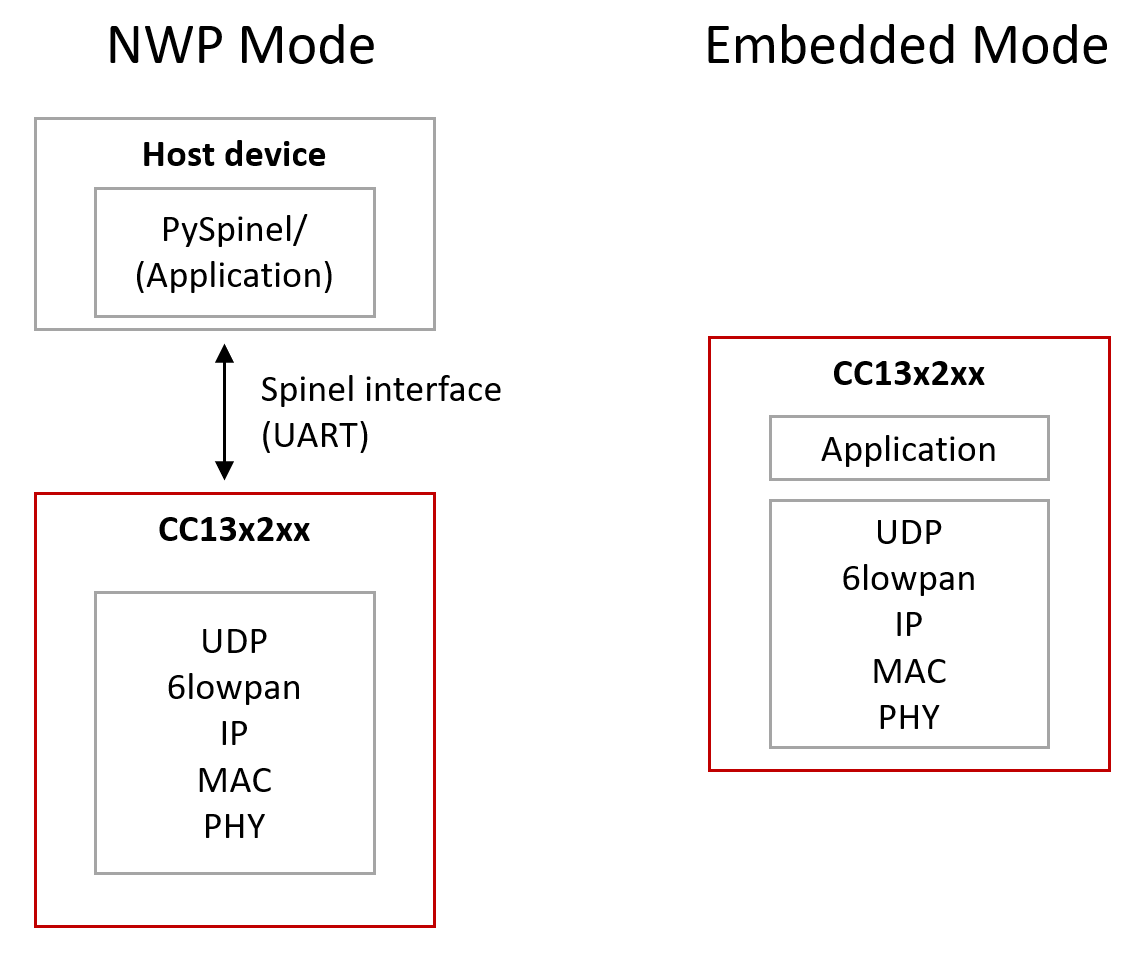
Figure 21. NWP and Embedded Configurations¶
A co-processor is shown in Figure 21. (left). The protocol stack runs on the device while the application is executed on an external MPU or MCU. The application interfaces with the device using the network protocol interface (NWP) over a serial universal asynchronous receiver/transmitter (UART) connection. This configuration is useful for cases where the application image is large. If the application is run from a host device, it will not be limited by the flash size of the device. The NWP interface is documented in the TI Wi-SUN FAN NWP Interface Guide.
A single device is shown in Figure 21. (right). The application and protocol stack are both implemented on the embedded device as a true single-chip solution.This configuration is the simplest and most common for network nodes.
Please see the Example Application Guide for availability of the modes on specific part numbers.