## Introduction
<br>
The MCU+ Software Development Kit (SDK) is a set of software development tools that enables engineers to develop applications on the Sitara MCU Platform. This powerful software toolkit provides a cohesive and consistent software experience by packaging essential software components and easy-to-use examples in one easy-to-use software package.
<hr>
## SDK Components
<br>
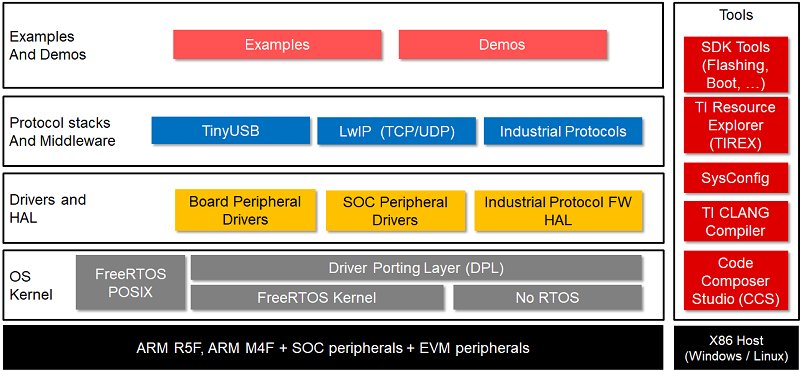
<br>
Starting from the bottom of this architecture diagram, the components are as follows:
* **Hardware**: The TI Sitara MCU Platform:
* **Arm R5F**: Single-core to quad-core Arm Cortex-R5F cores for real-time compute.
* **Arm M4F**: Single-core Arm Cortex-M4F core for safety applications.
* **SOC Peripherals**: Device-specific peripherals, such as GPIO and I2C.
* **EVM Peripherals**: Board-specific peripherals, such as on-board LEDs and Flash.
* **OS Kernel**: The kernel provides services such as timing and scheduling of tasks. The MCU+ SDK comes with the FreeRTOS Kernel. Using a kernel is optional - the SDK also supports the “NoRTOS” option, i.e. bare-metal, which allows the Drivers to be used with no underlying OS. For more details on FreeRTOS versus NoRTOS, see [FreeRTOS Basics](freertos.html).
* The **Driver Porting Layer (DPL)** abstracts driver interfaces. Drivers use OS and CPU features such as clocks, interrupts, and semaphores. By abstracting this functionality, applications using the drivers are independent of the OS and CPU and can use either the FreeRTOS Kernel or no RTOS.
* The **POSIX** layer abstracts the RTOS kernel functionality used by applications. The POSIX layer allows examples and user applications to be easily ported to use a different kernel. Using this layer is optional.
* **Drivers**: Exposes functionality of SOC and board peripherals in a consistent manner across all MCU+ devices. Even though the underlying hardware implementation may differ across MCU+ devices, the Driver APIs remain consistent so the same code can be re-used across the Sitara MCU Platform.
* **Protocol Stacks and Middleware**: Software stacks that provide additional functionality on top of the Drivers. Profinet and TinyUSB are examples of Protocol Stacks and Middleware.
* **Examples and Demos**: The SDK provides a wide range of examples. Their purpose is to make it easy to start writing applications. Each example comes with its own documentation and project files. Examples are provided that use the FreeRTOS kernel or no RTOS.
* **Tools**: The SDK provides various tools to assist with development. For example, tools for flashing and booting are provided in the SDK.
<hr>
## Directory Structure
<br>
The SDK is installed in `/ti` or `C:\ti` by default. This is also the default installation location for any components that are installed alongside the SDK. This is the top-level directory structure of the SDK installation:
<br>
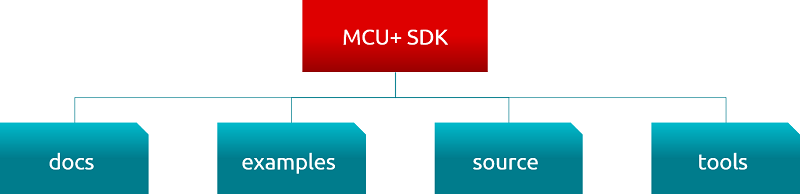
<br>
* The **docs** directory contains all of the documentation for the MCU+ SDK, including the User's Guide and API Guide.
* The **examples** directory contains a number of example applications for each supported EVM or LaunchPad.
* The **source** directory contains source code and libraries used when building applications. This includes files for drivers, boards, devices, middleware, and more. For example, the source code for all of the drivers are provided here.
* The **tools** directory contains a number of tools for supporting various functionalities needed for the device.
Since the same directory structure is used across MCU+ SDKs, it is possible to move application code between different devices without making significant changes to the file structure or include paths.
<hr style="width:50%; margin: auto;" />
### Examples Directory
The following figure similarly provides an overview of the “examples” directory contents that are common to all device types.
<br>
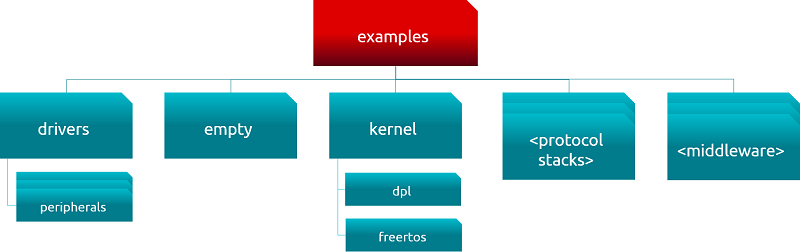
<br>
<hr style="width:50%; margin: auto;" />
### Source Directory
The following figure shows a high-level view of the “source” directories that are common to all device types.
<br>
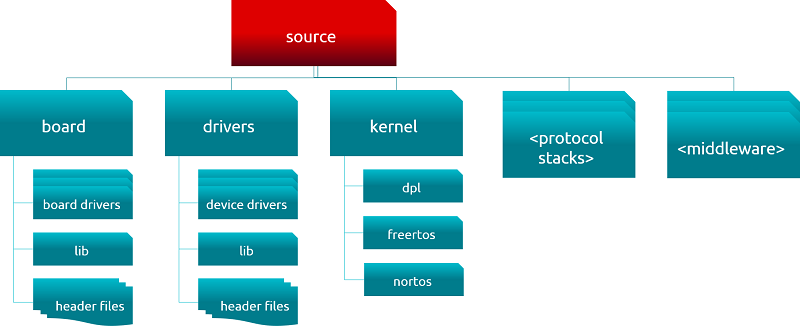
<br>
<hr>
## Tools and Components NOT Included in the SDK
<br>
**Code Composer Studio (CCS)**: Code Composer Studio is an integrated development environment (IDE) composed of a suite of tools used to develop and debug embedded applications for the Sitara MCU Platform.
**TI Resource Explorer (TIREX)**: TI Resource Explorer is a web-based tool for browsing and accessing contents of software packages in the cloud without the need to download the entire package. TIREX is delivered integrated in CCS or can be used via the [TI DevTools](https://dev.ti.com) portal.
**SysConfig**: SysConfig is an intuitive and comprehensive collection of graphical utilities for configuring pins, peripherals, subsystems, and other components. The tool's output includes C header and source files that are used to configure and build MCU+ SDK applications. The SysConfig tool is delivered integrated in CCS, as a standalone installer, or can be used via the [TI DevTools](https://dev.ti.com) portal. It has both a Graphical User Interface (GUI) and a Command Line Interface (CLI).
**TI Arm Clang Compiler Tools**: TI Arm® Clang Compiler Tools is derived from the open-source clang compiler and its supporting LLVM infrastructure and supports development of applications for the Sitara MCU Platform.
**UniFlash**: UniFlash is a standalone tool used to program on-board memory (flash) on Sitara MCUs. It has a Graphical User Interface (GUI), a Command Line Interface (CLI), and a scripting interface.
<br>
Please see the [MCU+ SDK Getting Started Guide](https://software-dl.ti.com/mcu-plus-sdk/esd/AM243X/latest/exports/docs/api_guide_am243x/GETTING_STARTED.html) for steps to install these components.
<hr>
## Project Types
<br>
There are two different example project types in the MCU+ SDK:
**Single-core project**: These are example projects that contain an application for a single core on an MCU+ device, such as the R5F core or M4F core.
**System project**: These are multi-core example projects that automatically bring in the example projects for every core on the device. The system project allows you to map single-core projects to device cores, to define the relationships between the single-core projects, and to specify system-wide pre/post-build steps.
<hr>
## Example Types
<br>
There are four different example types in the MCU+ SDK:
**Drivers**: These are examples that showcase drivers for the various peripherals on an MCU+ device.
**Kernel**: These are examples that showcase kernel-level drivers such as FreeRTOS and DPL.
**Networking**: These are examples that showcase the various Industrial Networking stacks provided in the SDK.
**Empty**: These are template projects that can be used as a starting point for developing applications using the SDK.
<hr>
## Libraries
<br>
The libraries in the SDK can be found in the `lib` folders of the various modules. For example, the Driver libraries are located in the `source/drivers/lib` folder.
They can be built in either `debug` or `release` mode. `Debug` mode is built without optimization and is recommended for stepping through code in CCS. `Release` mode is built with optimization and provides the best performance.
The libraries use the following naming convention:
* `<module>.<device>.<core>.<compiler>.<build-profile>.lib.`
* For example: `drivers.am243x.r5f.ti-arm-clang.debug.lib.`
<hr style="width:50%; margin: auto;" />
### Common libraries needed in an MCU+ SDK application
<br>
* **Drivers** - The drivers library is needed to use the device peripheral drivers, such as the GPIO driver.
* **NoRTOS/FreeRTOS** - The noRTOS or FreeRTOS libraries are needed to use the OS-specific APIs, such as Semaphores.
* **Board** - The board library is needed to use the board peripheral drivers, such as the Flash or LED drivers.
<hr style="width:50%; margin: auto;" />
### Rebuilding Libraries
<br>
All SDK libraries come pre-built with both **debug** and **release** options. The libraries need to be rebuilt whenever changes to the driver source code are made.
{{r **Note:** Rebuilding a CCS project does NOT rebuild the libraries.
}}
To re-build the libraries, perform the following commands in a command prompt or terminal.
```bash
cd <SDK_INSTALL_DIR>
gmake -s libs PROFILE=release
```
To clean the libraries, perform the following commands in a command prompt or terminal.
```bash
cd <SDK_INSTALL_DIR>
gmake -s libs-clean PROFILE=release
```
* `-s` denotes silent build option.
The libraries can also be built with `PROFILE=debug` to build without optimization. This is useful when debugging code in CCS.
Note, the `<SDK_INSTALL_DIR>` contains a makefile - open this makefile in a text editor to view all of the supported build targets.
<hr>
## Starting a New MCU+ SDK Application
<br>
{{r **Note:** Do not use the New CCS Project Wizard.
}}
<br>
Start with one of the example projects or the Empty Project Template within the SDK. Each software component in the SDK comes with its own set of examples. All of the necessary include paths, SDK-specific defines, and build settings are already part of the Empty Project Template
<hr>
## []{ } Knowledge Check
<br>
**1. True or False:** The MCU+ SDK provides a POSIX layer that can be used to abstract FreeRTOS kernel functionality.
[quiz]
v True --> Correct!
x False --> Incorrect
[quiz]
<br>
**2. True or False:** The MCU+ SDK provides examples and demos that use the FreeRTOS kernel or no RTOS.
[quiz]
v True --> Correct!
x False --> Incorrect
[quiz]
<br>
**3. True or False:** To create a new MCU+ SDK application, use the CCS New Project Wizard.
[quiz]
x True --> Incorrect
v False --> Correct!
[quiz]
<hr>
## Next Steps
<br>
Now that you have been introduced to the MCU+ SDK, you can progress to the next module where you will learn about a typical MCU+ SDK project.
##### [Part 2: Understanding an MCU+ SDK Project >](mcu_plus_application.html)
<br>
<hr>
## Additional Reading
##### [MCU+ SDK User Guide](https://software-dl.ti.com/mcu-plus-sdk/esd/AM243X/latest/exports/docs/api_guide_am243x/index.html)
<br>
<hr>
<div align="center" style="margin-top: 4em; font-size: smaller;">
<a rel="license" href="https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/"><img alt="Creative Commons License"
style="border-width:0" src="..//web_support/cc_license_icon.png" /></a><br />This work is licensed under a <a
rel="license" href="https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/">Creative Commons
Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License</a>.</div>