SmartRF Protocol Packet Sniffer¶
A CC13xx or CC26xx Launchpad can be used as packet sniffer device for TI 15.4-Stack radio packets. This feature enables easier development and debugging for those developing products with the TI 15.4-Stack. This section provides details on the required software, where to get it, and how to set it up to sniff over-the-air (OTA) traffic. Wireshark™ is the recommended packet sniffer.
SmartRF Packet Sniffer 2 software is available to download here: http://www.ti.com/tool/packet-sniffer
For detailed information regarding the installation and setup of hardware and software for SmartRF Packet Sniffer 2, visit the User Guide here: http://software-dl.ti.com/lprf/packet_sniffer_2/docs/user_guide/html/index.html
Configure for ARIB Mode¶
Please use the following configuration when sniffing ARIB mode. (For more information on this mode, please see ARIB Regulation Type.)
Open the sniffer agent and select Device Configuration as described in the Packet Sniffer User’s Guide.
Configure Wi-SUN PHY #4a (ID 6)
Select base frequency 920.7 MHz.
Select your channel. Channel 0 corresponds to 920.7 MHz, i.e. the channel called 24,25 in SysConfig. Channel 1 corresponds to 920.9 MHz, i.e. the channel called 25,26 in SysConfig. Etc.
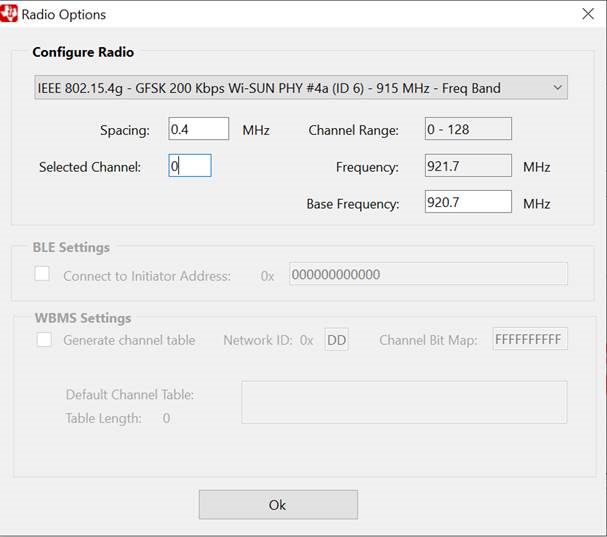
Figure 80. Configure Packet Sniffer for ARIB mode.¶
Non-beacon Mode Example Sniffer Output¶
Figure 81. shows the SmartRF Packet Sniffer 2 output on Wireshark™ for our default sensor and collector example, which configures a non-beacon network at 50kbps PHY.
The capture shows a beacon request sent by the sensor to any listening collectors. The collector then responds with a beacon and the sensor follows by sending an association request. When the collector receives the request, the pair exchange metadata and the collector finally sends the association response. Figure 82. shows the full association response packet information as displayed on Wireshark™.
For more information regarding the association sequence, see Non-Beacon Mode.
Figure 81. Packet Sniffer 2 capture of sensor association in Non-Beacon mode at 50kbps PHY¶
Figure 82. Wireshark™ dissection of association response packet in Non-Beacon mode¶
Beacon Mode Example Sniffer Output¶
Figure 83. shows the SmartRF Packet Sniffer 2 output on Wireshark™ for a modified sensor and collector example, which configures a beacon enabled network at 50kbps PHY.
The capture shows a beacon requests sent by the coordinator. The sensor then responds by sending an association request. When the collector receives the request, the pair exchange metadata and the collector finally sends the association response. For more information regarding the association sequence, see Beacon Enabled Mode.
Figure 83. Wireshark™ capture of sensor association in Beacon mode at 50kbps PHY¶
Warning
It is not possible to sniff multiple channels at one time using a single instance of SmartRF Packet Sniffer 2. For this reason, it is not possible to sniff a Frequency-hopping configured network.
One can reduce the channels enabled in the channel mask in FH mode to sniff fewer channels. Then, using multiple Packet Sniffer instances, one can see the traffic across multiple channels. Note, this requires a single Launchpad per channel desired to sniff.